Piezo Material Overview
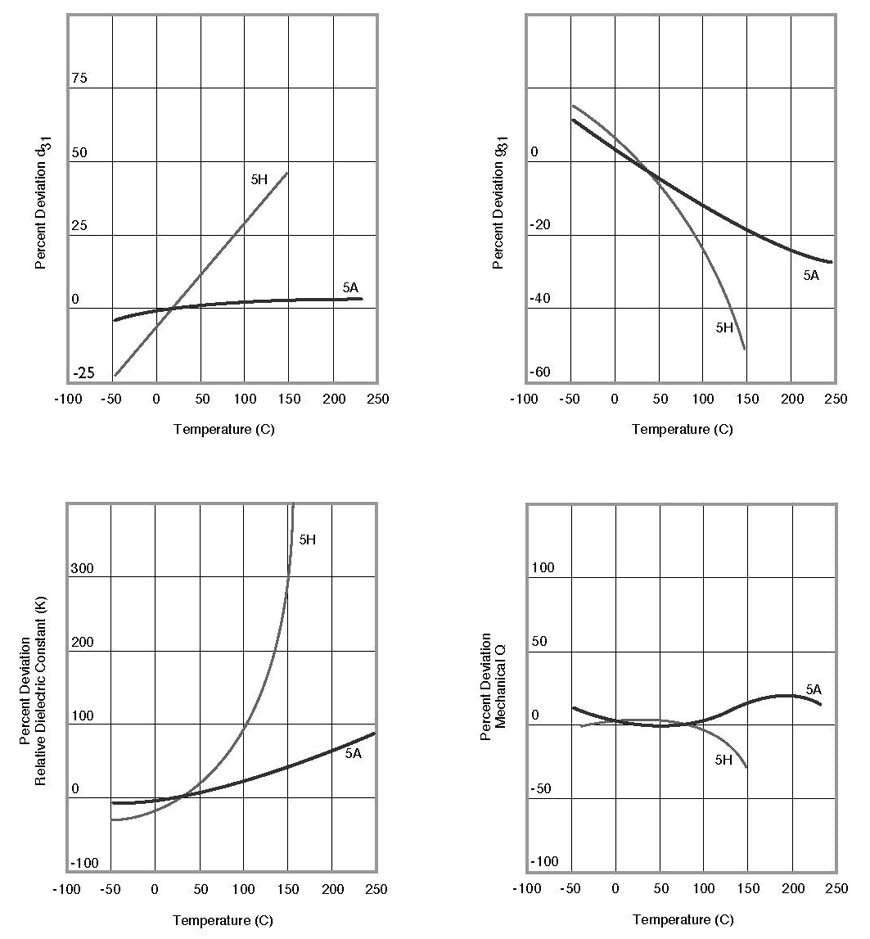
PSI-5A4E is an industry type 5A (Navy Type II) piezoceramic. Thin vacuum sputtered nickel electrodes produce extremely low current leakage and low magnetic permeability. It operates over a wide temperature range and is relatively temperature insensitive.
When an electric field having the same polarity and orientation as the original polarization field is placed across the thickness of a single sheet of piezoceramic, the piece expands along the axis of polarization (thickness direction) and contracts perpendicular to the axis of polarization (length and width direction). The motion in the thickness direction is on the order of tens of nanometers. Motion in the length direction is typically on the order of microns or tens of microns.
Overview of 5A
- DOD Type II, Lead-Zirconate Titanate
- High strain (charge) constants, permittivity, and coupling constants
- Low mechanical quality factor
- High Curie temperature extends its temperature range and thermal stability
- High charge output useful for sensing devices and generator elements
- High strain output useful for large displacements at modest voltages
- Used for sensing (receivers, knock, acoustic, musical pick-ups, vibration, vortex, material testing)
- Used for actuators (valves, positioning, vibrating, AFM, fans, tilters)
PSI-5H4E is an industry type 5H (Navy Type VI) piezoceramic. Thin vacuum sputtered nickel electrodes produce extremely low current leakage and low magnetic permeability. It has high motion per volt sensitivity but its upper temperature range is limited and its properties are more sensitive to temperature.
When an electric field having the same polarity and orientation as the original polarization field is placed across the thickness of a single sheet of piezoceramic, the piece expands along the axis of polarization (thickness direction) and contracts perpendicular to the axis of polarization (length and width direction). The motion in the thickness direction is on the order of tens of nanometers. Motion in the length direction is typically on the order of microns or tens of microns.
Overview of 5H
- DOD Type VI, Lead-Zirconate Titanate
- Very high strain (charge) constants, permittivity, and coupling constants
- Modest Curie temperature restricts its temperature range and thermal stability
- Low mechanical quality factor
- High charge output useful for sensing devices and generator elements
- High strain output useful for large displacements at lower voltages
- Used for sensing (receivers, knock, hydrophones, pick-ups, medical diagnostics)
- Used for actuators (valves, positioning, fans, tilters)
PSI-5J1E is an industry type 5J (Navy Type V) piezoceramic. Thin vacuum sputtered silver electrodes produce extremely low current leakage and low magnetic permeability. This material provides a compromise between PZT 5A and 5H.
Single Crystal PMN-PT is an electromechanically active crystal which has a combination of piezoelectric and electrostrictive properties resulting in superior electromechanical conversion properties. Unlike our familiar piezos which are created as sintered blocks of ceramic, PMN-PT starts life as a large pure crystal artificially grown slowly out of a melt. It is inherently different that piezoceramic both in application and in handling, and therefore should not be thought of as a 'drop in' replacement of piezoceramic parts, but rather as 'ground up' design option for applications requiring higher energy density than possible with piezoceramics.
| PIEZO.COM'S Designation | Symbol | Units | PSI-5A4E | PSI-5J1E | PSI-5H4E | SINGLE CRYSTAL PIEZO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIEZOELECTRIC | ||||||
| Industry Designations | Navy type II; Industry Type 5A | Navy type V; Industry Type 5J | Navy type VI; Industry Type 5H | PMN-PT | ||
| Composition | Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) | Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) | Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) | |||
| Relative Dielectric Constant (@ 1 KHz) | KT3 | 1800 | 2100 | 3800 | 4753 | |
| Piezoelectric "d" coefficients relate the Strain Produced / Electric Field Applied or the Short Circuit Charge Density Produced / Stress Applied | ||||||
| d33 | meter/Volt or Coulomb/Newton |
390 x 10-12 | 500 x 10-12 | 650 x 10-12 | 1285-12 pC/N | |
| d31 | meter/Volt or Coulomb/Newton |
-190 x 10-12 | -210 x 10-12 | -320 x 10-12 | -646-12 pC/N | |
| Piezoelectric "g" coefficients relate the Open Circuit Electric Field Produced / Stress Applied or the Strain Produced / Charge Density Applied | ||||||
| g33 | Volt-meter/Newton or meter2/Coulomb |
24.0 x 10-3 | 23.0 x 10-3 | 19.0 x 10-3 | 30.55-3 Vm/N | |
| g31 | Volt-meter/Newton or meter2/Coulomb |
-11.6 x 10-3 | -10.4 x 10-3 | -9.5 x 10-3 | -15.36-3 Vm/N | |
| Coupling Coefficient | k33 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.89 | |
| k31 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.46 | ||
| Polarizing Field | Ep | Volt/meter | > 2 x 106 | > 1.7 x 106 | > 1.5 x 106 | |
| Initial Depolarizing Field | Ec | Volt/meter | ~ 5 x 105 | ~ 4 x 105 | ~ 3 x 105 | |
| Coercive Field | Ec | Volt/meter | ~ 1.2 x 106 | ~ 1.0 x 106 | ~ 8 x 105 | 4.5-6 kV/cm |
| MECHANICAL | ||||||
| Density | δ | Kg/meter3 | 7800 | 7800 | 7800 | 8.12 g/cc |
| Mechanical Q | 80 | 60 | 32 | ~150 | ||
| Elastic Modulus | YE3 | Newton/meter2 | 5.2 x 1010 | 5.1 x 1010 | 5.0 x 1010 | 2.0410 N/m2 |
| YE1 | Newton/meter2 | 6.6 x 1010 | 6.4 x 1010 | 6.2 x 1010 | 2.1810 N/m2 | |
| THERMAL | ||||||
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | meter/meter °C | ~ 4 x 10-6 | ~ 4 x 10-6 | ~ 3 x 10-6 | ~10-6/°C | |
| Curie Temperature | °C | 350 | 320 | 230 | 140-170°C | |
Piezoelectric Properties